Saka Wikipédia Jawa, bauwarna mardika basa Jawa
Student’s t
Probability density function
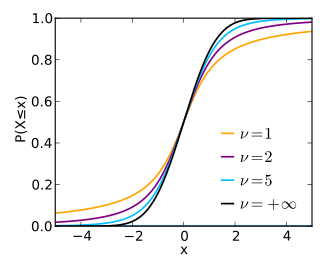
Cumulative distribution function
Parameters
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
degrees of freedom (real )
Support
x ∈ (−∞; +∞)
PDF
Γ
(
ν
+
1
2
)
ν
π
Γ
(
ν
2
)
(
1
+
x
2
ν
)
−
ν
+
1
2
{\displaystyle \textstyle {\frac {\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu +1}{2}}\right)}{{\sqrt {\nu \pi }}\,\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)}}\left(1+{\frac {x^{2}}{\nu }}\right)^{-{\frac {\nu +1}{2}}}\!}
CDF
1
2
+
x
Γ
(
ν
+
1
2
)
⋅
2
F
1
(
1
2
,
ν
+
1
2
;
3
2
;
−
x
2
ν
)
π
ν
Γ
(
ν
2
)
{\displaystyle {\begin{matrix}{\frac {1}{2}}+x\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu +1}{2}}\right)\cdot \\[0.5em]{\frac {\,_{2}F_{1}\left({\frac {1}{2}},{\frac {\nu +1}{2}};{\frac {3}{2}};-{\frac {x^{2}}{\nu }}\right)}{{\sqrt {\pi \nu }}\,\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)}}\end{matrix}}}
2 F 1 is the hypergeometric function
Mean
0 for
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Median
0
Mode
0
Variance
ν
ν
−
2
{\displaystyle \textstyle {\frac {\nu }{\nu -2}}}
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Skewness
0 for
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Ex. kurtosis
6
ν
−
4
{\displaystyle \textstyle {\frac {6}{\nu -4}}}
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Entropy
ν
+
1
2
[
ψ
(
1
+
ν
2
)
−
ψ
(
ν
2
)
]
+
log
[
ν
B
(
ν
2
,
1
2
)
]
{\displaystyle {\begin{matrix}{\frac {\nu +1}{2}}\left[\psi \left({\frac {1+\nu }{2}}\right)-\psi \left({\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)\right]\\[0.5em]+\log {\left[{\sqrt {\nu }}B\left({\frac {\nu }{2}},{\frac {1}{2}}\right)\right]}\end{matrix}}}
MGF
undefined
CF
K
ν
/
2
(
ν
|
t
|
)
(
ν
|
t
|
)
ν
/
2
Γ
(
ν
/
2
)
2
ν
/
2
−
1
{\displaystyle \textstyle {\frac {K_{\nu /2}\left({\sqrt {\nu }}|t|)({\sqrt {\nu }}|t|\right)^{\nu /2}}{\Gamma (\nu /2)2^{\nu /2-1}}}}
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Sajeroning probabilitas lan statistika , Distribusi t-student utawa Student’s t -distribution (asring dicekak dadi t -distributioncontinuous probability distribution sing dianggo nalika nganakaké èstrimasi aji rata-rata (mean ) saka sawijining populasi sing ukuran sampel é cilik lan standard déviasi ora diweruhi.
Fungsi dhènsitas probabilitas saka distribusi t-Student sing standard ya iku:
f
(
t
)
=
Γ
(
ν
+
1
2
)
ν
π
Γ
(
ν
2
)
(
1
+
t
2
ν
)
−
ν
+
1
2
,
{\displaystyle f(t)={\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {\nu +1}{2}})}{{\sqrt {\nu \pi }}\,\Gamma ({\frac {\nu }{2}})}}\left(1+{\frac {t^{2}}{\nu }}\right)^{-{\frac {\nu +1}{2}}},\!}
ing ngendi
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
drajad kabébasan
Γ
{\displaystyle \Gamma }
fungsi Gamma . Bisa uga ditulis:
f
(
t
)
=
1
ν
B
(
1
2
,
ν
2
)
(
1
+
t
2
ν
)
−
ν
+
1
2
,
{\displaystyle f(t)={\frac {1}{{\sqrt {\nu }}\,B\left({\frac {1}{2}},{\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)}}\left(1+{\frac {t^{2}}{\nu }}\right)^{-{\frac {\nu +1}{2}}}\!,}
ing ngendi B iku wujud fungsi Beta .
Kanggo
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Γ
(
ν
+
1
2
)
ν
π
Γ
(
ν
2
)
=
(
ν
−
1
)
(
ν
−
3
)
⋯
5
⋅
3
2
ν
(
ν
−
2
)
(
ν
−
4
)
⋯
4
⋅
2
.
{\displaystyle {\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {\nu +1}{2}})}{{\sqrt {\nu \pi }}\,\Gamma ({\frac {\nu }{2}})}}={\frac {(\nu -1)(\nu -3)\cdots 5\cdot 3}{2{\sqrt {\nu }}(\nu -2)(\nu -4)\cdots 4\cdot 2\,}}.}
Kanggo
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Γ
(
ν
+
1
2
)
ν
π
Γ
(
ν
2
)
=
(
ν
−
1
)
(
ν
−
3
)
⋯
4
⋅
2
π
ν
(
ν
−
2
)
(
ν
−
4
)
⋯
5
⋅
3
.
{\displaystyle {\frac {\Gamma ({\frac {\nu +1}{2}})}{{\sqrt {\nu \pi }}\,\Gamma ({\frac {\nu }{2}})}}={\frac {(\nu -1)(\nu -3)\cdots 4\cdot 2}{\pi {\sqrt {\nu }}(\nu -2)(\nu -4)\cdots 5\cdot 3\,}}.\!}
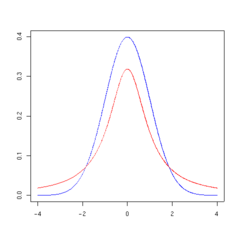
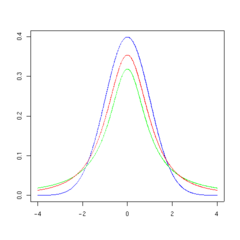
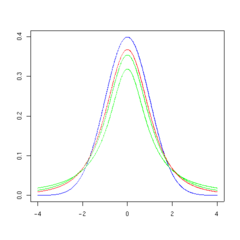
Gambar-gambar iki nuduhaké dhènsitas saka t -distribution tumrap aji
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
t -distribution (garis abang) dadi luwih cedhak marang dhistribusi normal nalika aji
ν
{\displaystyle \nu }
Density of the t -distribution (red) for 1, 2, 3, 5, 10, and 30 df compared to the standard normal distribution (blue).
1 degree of freedom 2 degrees of freedom 3 degrees of freedom
5 degrees of freedom 10 degrees of freedom 30 degrees of freedom
Mixed continuous-discrete univariate distributions
Designing studies
Uncontrolled studies




![{\displaystyle {\begin{matrix}{\frac {1}{2}}+x\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu +1}{2}}\right)\cdot \\[0.5em]{\frac {\,_{2}F_{1}\left({\frac {1}{2}},{\frac {\nu +1}{2}};{\frac {3}{2}};-{\frac {x^{2}}{\nu }}\right)}{{\sqrt {\pi \nu }}\,\Gamma \left({\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)}}\end{matrix}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/02732e546784af1fb16d0dc1bb65dd743e2284ad)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{matrix}{\frac {\nu +1}{2}}\left[\psi \left({\frac {1+\nu }{2}}\right)-\psi \left({\frac {\nu }{2}}\right)\right]\\[0.5em]+\log {\left[{\sqrt {\nu }}B\left({\frac {\nu }{2}},{\frac {1}{2}}\right)\right]}\end{matrix}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8d02573057e45a7d497ab31ced38dbd9a5901f77)